The world of finance can be intimidating, with complex terms and intricate strategies that seem designed to confuse. But amidst the jargon lies a powerful tool, one that can potentially amplify both risk and reward: options trading. I remember my first tentative steps into the world of options, armed with a textbook and a healthy dose of skepticism. I was overwhelmed by the myriad of strategies, the volatility of the market, and the sheer complexity of it all. However, as I delved deeper, I began to appreciate the flexibility and potential of options trading. This article aims to demystify the process, providing practical examples and insights to help you navigate the world of options confidently.
Image: www.asktraders.com
For someone new to the world of options, the concept can feel like venturing into uncharted territory. Imagine a world where you can buy the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price within a specific time frame. That’s the essence of options trading. It allows you to participate in the market’s swings without necessarily owning the underlying asset, introducing a level of leverage and flexibility not found in traditional stock trading.
Understanding Options Contracts: A Glimpse into the World of Derivatives
Defining Options Contracts
At its core, an options contract is a derivative financial instrument that grants the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specific price (strike price) on or before a certain date (expiration date). Unlike stocks, which represent ownership, options are essentially contracts that derive their value from the underlying asset. There are two main types of options:
- Call options give the buyer the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price.
- Put options give the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price.
Options trading can be used for various purposes, including:
- Speculation: Profiting from anticipated price movements in the underlying asset.
- Hedging: Mitigating potential losses in a portfolio.
- Income generation: Generating passive income through options premiums.
The Mechanics of Option Trading
The price of an options contract is known as the premium. This premium is influenced by several factors, including:
- Underlying asset price: The higher the price of the underlying asset, the more valuable a call option becomes and the less valuable a put option becomes.
- Strike price: The closer the strike price is to the current price of the underlying asset, the higher the premium.
- Time to expiration: The longer the time to expiration, the higher the premium. This is because there is a greater chance of the underlying asset price moving in the holder’s favor.
- Volatility: The higher the volatility of the underlying asset, the higher the premium. This is because there is a greater chance of large price movements, increasing the likelihood of a profit or loss.
Options contracts are traded on exchanges, similar to stocks, and typically have standardized terms. The options market offers a wide range of choices, allowing traders to tailor strategies to their specific risk tolerance and investment goals.
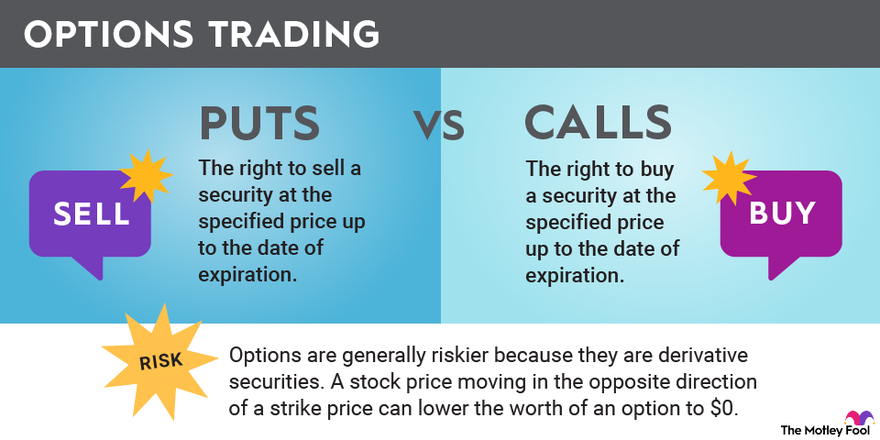
Image: www.fool.com
Examples of Options Trading Strategies
The beauty of options lies in their versatility. They offer a wealth of strategies for different market conditions and investment objectives. Here are some common examples:
1. Covered Call Writing
Imagine you own 100 shares of Apple stock. Instead of simply holding those shares, you decide to write a covered call option. This means you sell a call option on those shares. The buyer of the call option has the right to purchase your shares at a specific price on or before the expiration date. If the stock price stays below the strike price, the call option will expire worthless, and you’ll keep the premium you received for selling it. However, if the price rises above the strike price, the option buyer will exercise their right to buy your shares, and you’ll be obligated to sell them at the strike price. This strategy is a way to generate income while limiting potential upside gains.
2. Protective Put
Picture this: You own 100 shares of Tesla stock, and you’re worried about the potential for a price drop. To protect your investment, you buy a put option. This gives you the right, but not the obligation, to sell your shares at a specific price on or before the expiration date. If the stock price falls below your strike price, you can exercise your put option and sell your shares at a higher price, limiting your potential losses. This strategy is a form of downside protection.
3. Straddle
Let’s say you believe the price of Amazon stock is about to make a big move, but you’re not sure which direction it will go. You could choose to buy both a call option and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date. This is known as a straddle. If the stock price moves significantly in either direction, you stand to profit; however, if the stock price remains relatively flat, you’ll lose money on the premiums paid for both options. This strategy is a way to profit from volatility.
Navigating the Volatility of Options Trading
Options trading can offer significant potential for both gains and losses. Unlike traditional stocks, options contracts have a limited life span, meaning they expire on a certain date. This introduces an element of time decay, which can erode the value of options over time. It’s crucial to understand the concepts of volatility, time decay, and leverage to make informed decisions.
Tips for Successful Options Trading
- Start Small: Begin with a small amount of capital and gradually increase your exposure as you gain more experience.
- Thorough Research: Educate yourself about the underlying asset, market conditions, and the specific options strategy you intend to implement.
- Risk Management: Develop a risk management plan and stick to it. This involves setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and understanding your maximum risk tolerance.
- Diversification: Spread your investments across different assets and strategies to reduce overall portfolio risk.
- Patience: Opting trading is not a get-rich-quick scheme. Be patient, execute your strategies with discipline, and avoid emotional decisions.
Expert Advice
- Consult a Financial Advisor: If you’re unsure about options trading, consider seeking advice from a qualified financial advisor who can assess your risk tolerance and investment goals.
- Focus on Education: Continuously learn and expand your knowledge about options trading. There are numerous resources available, including books, articles, and online courses.
- Practice with Paper Trading: Simulate real-world trading scenarios using a paper trading account before risking real money.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Is options trading suitable for everyone?
A: No, options trading is generally considered more complex and riskier than traditional stock trading. It’s not suitable for everyone and is best suited for experienced traders who understand the intricacies of the market and have a strong risk management strategy.
Q: What are some of the risks associated with options trading?
A: Options trading involves various risks, including:
- Unlimited Risk: Unlike stocks, where your loss is limited to the purchase price of the shares, options contracts can lead to unlimited losses. This is because the price of the underlying asset can potentially move indefinitely.
- Time Decay: As the expiration date approaches, the value of options contracts typically declines. This is known as time decay, and it can erode the value of your investment even if the underlying asset price remains unchanged.
- Volatility: High volatility can amplify both potential gains and potential losses. While it can benefit some strategies, it can also increase the risk of losses.
Q: How can I learn more about options trading?
A: There are many resources available to help you learn about options trading. You can find books, articles, online courses, and even seminars offered by financial institutions and educational platforms.
Trading Options Examples
Conclusion
Options trading can provide a powerful tool for enhancing returns and mitigating risk. Understanding the basics of options contracts, exploring strategies like covered call writing and protective puts, and managing risk effectively are crucial for navigating this complex financial instrument. Remember to start small, do your research, and learn from experienced traders.
Are you interested in delving deeper into the world of options trading, exploring specific strategies, or discussing advanced concepts? Let us know! We are here to help you unravel the mysteries of this exciting realm.






