Introduction:
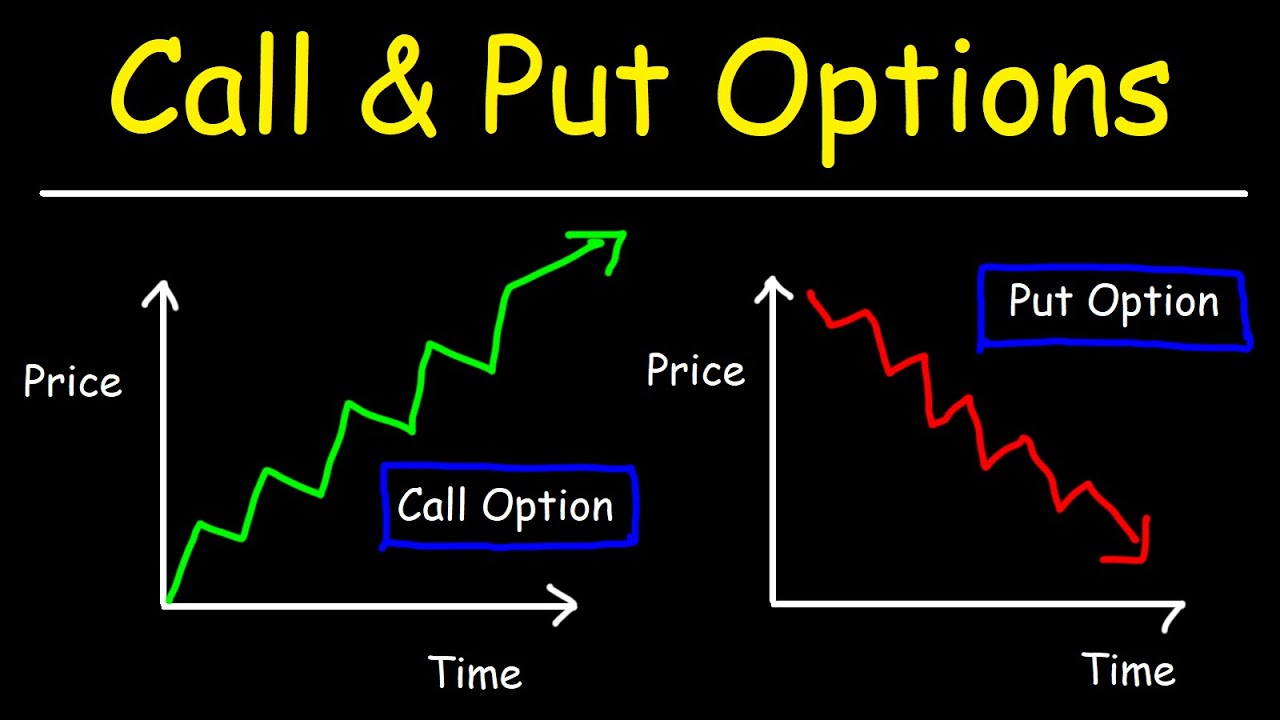
Image: www.youtube.com
Imagine harnessing the power of the financial markets to potentially boost your financial well-being. Option trading, a sophisticated yet accessible realm of investing, offers you that opportunity. Dive into this comprehensive guide to unravel the fundamentals of option trading, empowering you to make informed decisions and navigate the financial landscape with confidence.
Understanding Option Trading:
An option contract grants the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) on or before a specific date (expiration date). Options provide traders with versatility, allowing them to speculate on price movements or hedge against risks.
Key Concepts:
- Call Option: Gives the holder the right to buy an asset at the strike price.
- Put Option: Grants the holder the right to sell an asset at the strike price.
- Premium: The price paid by the option buyer to acquire the contract.
- Expiration Date: The last day the option contract can be exercised.
- Intrinsic Value: The difference between the underlying asset’s price and the strike price (positive for in-the-money options).
- Time Value: The premium paid for an option’s remaining time until expiration.
Types of Options:
Options can be classified based on their underlying asset:
- Stock Options: Contractual agreements tied to the price movements of stocks.
- Index Options: Linked to the value of market indices like the S&P 500 or Nasdaq 100.
- Commodity Options: Provide exposure to the fluctuating prices of raw materials like gold or crude oil.
- Currency Options: Offer the opportunity to profit from changes in foreign exchange rates.
Mechanics of Option Trading:
- Option Chain: Displaying all available options for a particular underlying asset, including their strike prices, expiration dates, and premiums.
- Open Position: When a trader buys or sells an option contract.
- Close Position: Exit strategy to offset the initial position, resulting in a profit or loss.
Strategies and Applications:
Options offer a myriad of strategies for traders with varying risk appetites and objectives. Popular options strategies include:
- Bullish Call Spread: Profitable when the underlying asset’s price rises.
- Bearish Put Spread: Benefits from price declines in the underlying asset.
- Covered Call: Strategy that involves selling a call option while holding the underlying asset.
- Protective Put: Used to protect against potential losses in long positions.
Expert Insights:
“Option trading can be a potent tool for informed investors, but it’s crucial to approach it with a comprehensive understanding and sound risk management principles.” – Dr. Marc Chandler, Chief Market Strategist, Bannockburn Global Forex.
Practical Applications:
Harnessing the power of options, investors can:
- Enhance potential returns through speculative trading.
- Hedge against downside risks to protect existing positions.
- Generate income through option premiums.
Conclusion:
Option trading presents a dynamic investment avenue, offering traders the potential to navigate market fluctuations and pursue financial growth. By grasping the basics, investors can unlock the opportunities inherent in options. Remember, a thorough understanding, prudent risk assessment, and a strategic approach are vital for success in option trading. Embrace this newfound knowledge and embark on your journey toward financial empowerment with confidence.

Image: tradingforexguide.com
Basic Knowledge Of Option Trading






