Introduction
Navigating the complex world of stock option trading can be daunting for beginners, especially when faced with a barrage of unfamiliar terminology. Understanding these terms is crucial for making informed decisions and maximizing your trading strategies. This comprehensive guide will delve into the essential stock option trading terminology, empowering you to navigate the market with confidence.

Image: s3.amazonaws.com
Before we embark on this terminological journey, let’s rewind to the formative years of my trading career. As a novice venturing into the world of options, I stumbled upon a plethora of unfamiliar terms that left me utterly bewildered. It was akin to stepping into a foreign language class without a dictionary.
Types of Stock Options
Call Options
Call options grant the option buyer the right, but not the obligation, to purchase a specified number of shares of a particular stock at a predetermined strike price on or before the expiration date. These options are typically purchased when the trader anticipates a rise in the underlying stock’s price.
Put Options
Put options, on the other hand, confer the right to sell a specified number of shares of a particular stock at a predetermined strike price on or before the expiration date. These options are typically purchased when the trader expects a decline in the underlying stock’s price.
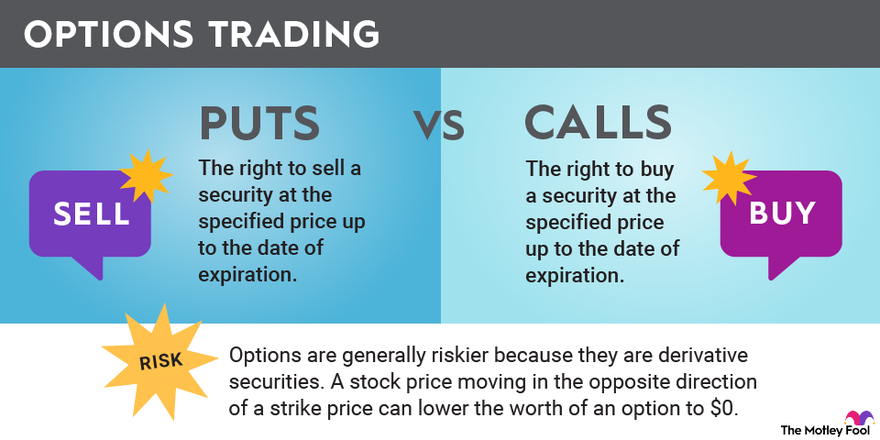
Image: runacrosscongo.org
Key Terminologies
Strike Price
The strike price is the predetermined price at which the option holder can purchase (call option) or sell (put option) the underlying shares.
Expiration Date
The expiration date is the date on which the option contract expires. Options can have various expiration dates, ranging from weekly to several months in the future.
Premium
The premium is the price paid by the option buyer to acquire the option contract. It represents the cost of the right to buy (call option) or sell (put option) the underlying shares.
In-The-Money (ITM)
An ITM option has an intrinsic value because its strike price is more favorable (lower for call options, higher for put options) than the current market price of the underlying stock.
At-The-Money (ATM)
An ATM option has no intrinsic value because its strike price is equal to the current market price of the underlying stock.
Out-of-The-Money (OTM)
An OTM option has no intrinsic value because its strike price is less favorable (higher for call options, lower for put options) than the current market price of the underlying stock.
Latest Trends and Developments
The stock option trading market is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and regulatory changes. Recent trends include:
- Increased Mobile Trading: Traders are increasingly using mobile apps to execute option trades, providing greater convenience and accessibility.
- Automated Trading: Algorithmic trading platforms allow traders to execute complex trading strategies more efficiently and quickly.
- Simplified Regulations: Regulators are working to make options trading more accessible for retail investors, such as reducing margin requirements.
Tips and Expert Advice
Based on my years of experience as a stock option trader, here are some invaluable tips and expert advice:
- Educate Yourself: Thoroughly research options trading before entering the market. Understand the different types of options, strategies, and risk management techniques.
- Start Small: Begin by trading small amounts until you gain confidence and experience. Overtrading can increase your risk and lead to significant losses.
- Set Realistic Expectations: Options trading involves risk and the potential for both profits and losses. Set realistic expectations and avoid chasing unrealistic returns.
- Manage Your Risk: Implement effective risk management strategies, such as stop-loss orders and position sizing, to limit potential losses.
- Learn from Mistakes: Every trader makes mistakes. Analyze your past trades, identify your errors, and learn from them to improve your future performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the difference between a call and a put option?
A: Call options give you the right to buy, while put options give you the right to sell, the underlying shares at a specific price on or before a certain date.
Q: What is the purpose of options trading?
A: Options trading allows you to speculate on the future price of a stock, hedge against potential losses, or generate income through premiums.
Q: Is options trading suitable for beginners?
A: Due to its complexity and risks, options trading may not be suitable for absolute beginners. It is recommended to gain a thorough understanding of the market before engaging in options trades.
Stock Option Trading Terminology
Conclusion
Understanding stock option trading terminology is paramount to unlocking the potential of this dynamic financial instrument. By mastering the terms, concepts, and strategies outlined in this guide, you can navigate the stock option market with greater confidence and make informed decisions. Remember, investing in options involves both rewards and risks, and it is essential to approach it with caution and a sound understanding of the underlying principles.
Are you intrigued by the world of stock option trading and eager to delve deeper into its complexities? Share your questions, thoughts, or experiences in the comments section below, and let’s continue the conversation.






