Introduction
Investing in the financial markets can be an exciting and potentially lucrative endeavor. Among the various investment options available, stocks and options stand out as two popular choices. While both offer opportunities for profit, they differ significantly in terms of their characteristics, risks, and rewards.

Image: www.vectorvest.com
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into a comparative analysis of stocks and options trading, empowering you with the knowledge to make informed investment decisions. We will explore their definitions, advantages, disadvantages, and strategies to help you navigate the complexities of these markets.
Understanding Stocks
A stock represents a fraction of ownership in a publicly traded company. When you purchase a stock, you become a shareholder entitled to a portion of the company’s profits (dividends) and voting rights in its governance. Stocks are typically bought and sold on stock exchanges, offering investors liquidity and the potential for both capital appreciation and dividends.
Understanding Options
An option, on the other hand, is a contract that gives you the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset (typically a stock or index) at a predetermined price within a specified period. Unlike stocks, options do not confer ownership rights. Instead, they derive their value from volatility and time decay.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Stocks
Advantages
- Potential for capital appreciation: Stocks have historically provided significant returns over the long term, benefiting from company growth and earnings.
- Dividend income: Shareholders are entitled to a portion of the company’s profits in the form of dividends.
- Diversification: Investing in stocks allows investors to diversify their portfolios and spread their risk.
Disadvantages
- Higher risk: Stocks are subject to market fluctuations and can experience price declines, leading to potential losses.
- Illiquidity: Some stocks may not have a high trading volume, making it challenging to buy or sell them quickly.
- Tax implications: Capital gains and dividends from stocks are subject to taxation, which can reduce overall returns.
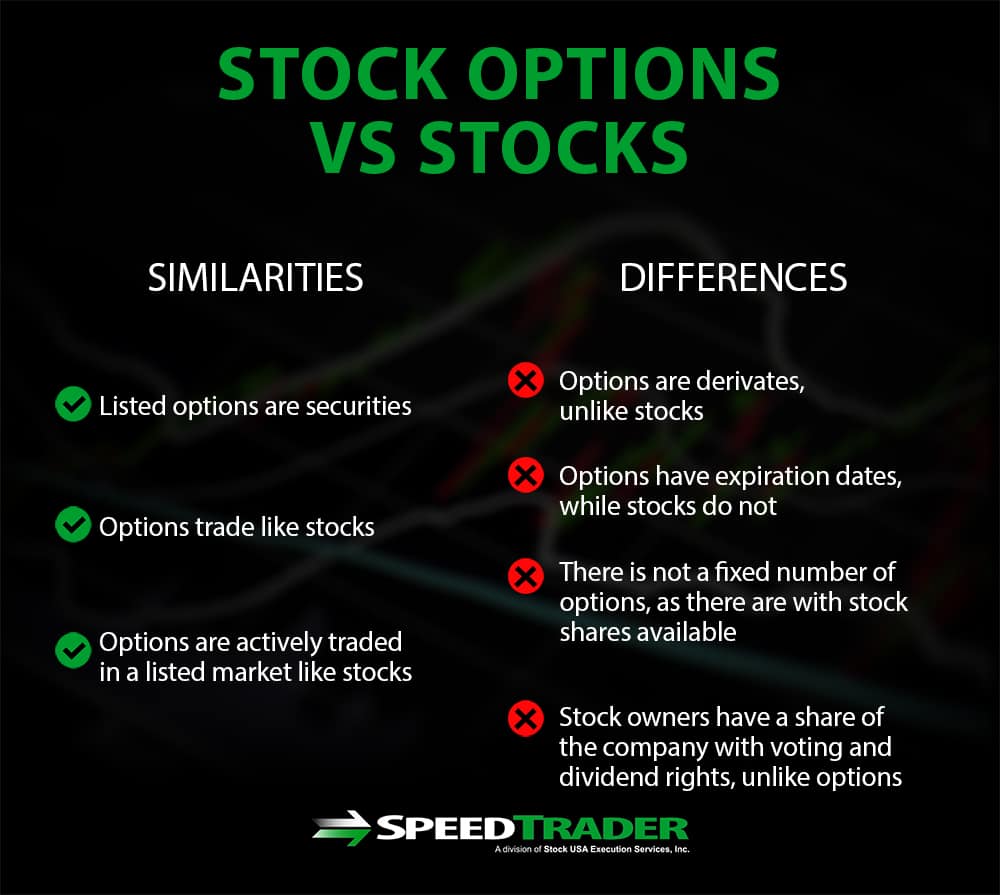
Image: speedtrader.com
Advantages and Disadvantages of Options
Advantages
- Leverage: Options provide investors with the ability to gain exposure to an underlying asset with less capital compared to buying the asset itself.
- Income generation: Selling options premiums can provide income while waiting for the underlying asset to move in a desired direction.
- Hedging: Options can be used to hedge against risk in existing stock positions or portfolios.
Disadvantages
- Limited upside: Profits from options are capped at a maximum level, unlike stocks, which have unlimited upside potential.
- Time decay: The value of options decays over time, even if the underlying asset does not decline.
- Complexity: Options trading requires a higher level of understanding and knowledge compared to stock investing.
Stock vs. Options Trading Strategies
Stock Trading Strategies
- Buy-and-hold strategy: Investing in a company with strong fundamentals and growth potential for long-term appreciation.
- Value investing: Purchasing undervalued stocks that are trading below their intrinsic value.
- Dividend investing: Focusing on stocks that provide consistent and growing dividends for income generation.
Options Trading Strategies
- Covered call: Selling a call option against a stock you own, earning a premium in exchange for the right to sell the stock at a higher price.
- Put selling: Selling a put option to someone who wants protection against a decline in the stock price, collecting a premium in the process.
- Bull call spread: Buying a call option at a lower strike price and selling a call option at a higher strike price, profiting from a rise in the underlying asset.
FAQs
Q: Which is a better investment: stocks or options?
A: The choice between stocks and options depends on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and knowledge. Stocks offer higher upside potential and long-term growth, while options provide leverage and versatility for income generation and hedging.
Q: Can I lose more money than I invested in options trading?
A: Yes, it is possible to lose more money than you invest in options trading, especially if you engage in aggressive strategies. Understanding risk management techniques and using stop-loss orders is crucial.
Q: How do I start stock or options trading?
A: Consult with a financial advisor, educate yourself on the markets, and research different trading platforms. Start with paper trading to practice and gain experience before investing real money.
Stocks Vs Options Trading

Image: seekingalpha.com
Conclusion
Stocks and options trading offer distinct opportunities and challenges in the financial markets. Stocks are suitable for long-term investors seeking diversification and capital appreciation, while options provide leverage and flexibility for experienced traders seeking income generation and hedging. By understanding their unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages, you can develop informed investment strategies that align with your financial goals. Are you interested in learning more about stocks vs. options trading?






