In the realm of investing, options trading often evokes a sense of intrigue and curiosity. While it holds the potential for high returns, it’s crucial to understand its complexities and approach it with prudence. This guide aims to unravel the intricacies of options trading, providing you with a roadmap to navigate this dynamic financial landscape.

Image: www.redfox-trading.com
What is Options Trading?
Options are contracts that grant traders the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price on a specified date. The underlying asset can be stocks, bonds, commodities, or even currencies. Options trading empowers traders with the flexibility to capitalize on or hedge against fluctuations in the underlying asset’s price.
Types of Options
There are two main types of options: calls and puts. Call options give traders the right to buy the underlying asset, while put options grant them the right to sell it. Each type of option can be further classified as either ‘in-the-money,’ ‘at-the-money,’ or ‘out-of-the-money,’ depending on the relationship between the current market price and the strike price (the predetermined price at which the option can be exercised).
How to Trade Options
To trade options, you need a brokerage account that supports options trading. Once you have an account, you can follow these general steps:
- Identify the underlying asset you want to trade.
- Choose an options contract with a strike price and expiration date that align with your trading strategy.
- Determine the number of contracts you want to buy or sell.
- Monitor the price of the underlying asset and the option contract.
- Close your position at a profit or loss once your trading objectives are met.
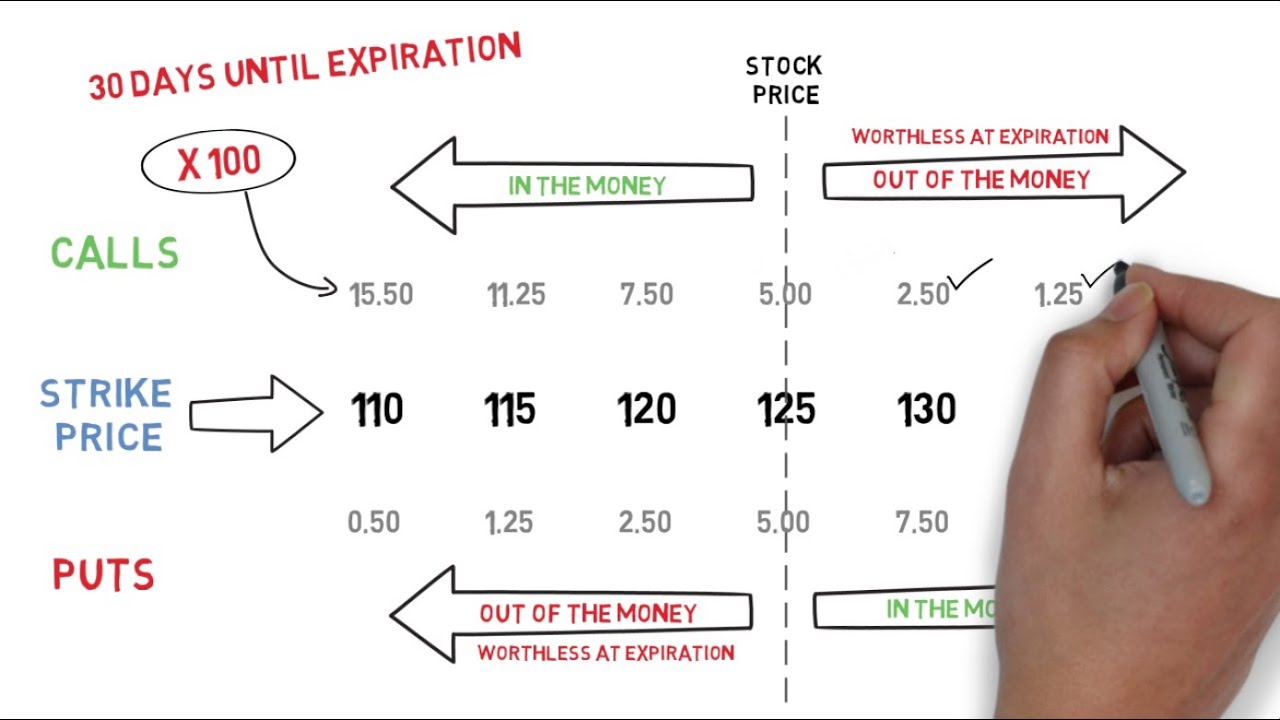
Image: www.youtube.com
Strategies for Options Trading
There are various options trading strategies that cater to different risk appetites and trading styles. Some common strategies include:
- Buying Calls: Purchasing call options bets on the underlying asset’s price rising.
- Buying Puts: Acquiring put options signifies a prediction of the underlying asset’s price decline.
- Selling Calls (Covered or Uncovered): Selling call options involves writing a contract to sell the underlying asset. Covered calls are backed by the underlying asset’s ownership, while uncovered calls may involve higher risk.
- Selling Puts (Cash-Secured or Naked): Selling put options creates an obligation to buy the underlying asset. Cash-secured puts require holding sufficient funds to cover potential purchases, while naked puts carry greater risk due to unlimited potential losses.
Expert Insights and Actionable Tips
As you embark on your options trading journey, it’s wise to heed the advice of experienced traders:
- “Options trading amplifies the potential for gains and losses. Understand your risk tolerance and manage your positions accordingly,” advises veteran trader John Carter.
- “Study the underlying asset and the option chain thoroughly. Don’t enter trades without proper research,” emphasizesoptionsstrategist Emily Duncan.
- “Stay disciplined and avoid emotional trading. Stick to your strategy and don’t let FOMO (fear of missing out) drive your decisions,” cautions financial educator Scott Bodiker.
How Do You Make Money With Options Trading

Image: perfydesign.blogspot.com
Conclusion
Options trading presents both opportunities and risks, requiring a thorough understanding of the market, risk management principles, and trading strategies. By embracing a strategic approach, conducting thorough research, and seeking guidance from reputable sources, you can harness the power of options trading to potentially enhance your financial portfolio and achieve your investment goals.
Remember, the world of options trading is vast and continually evolving. This article serves as a stepping stone to further exploration. Consult with a financial advisor or reputable educational platform to gain a comprehensive understanding and develop a personalized trading strategy.






