Have you ever felt the pang of anxiety as your stock portfolio plunges downwards, witnessing the painstaking erosion of your hard-earned savings? What if there was a strategy that could not only offer protection against such market downturns but also potentially generate profits during these periods of volatility? Enter the world of put options, a powerful financial instrument that can help you navigate the unpredictable landscape of the stock market.
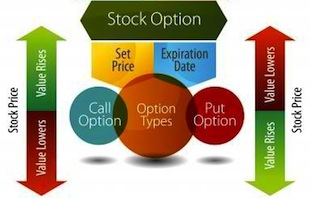
Image: www.seeitmarket.com
Put options are a type of derivative contract that grants the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price (known as the strike price) on or before a specified date (the expiration date). This right can be invaluable when you believe the price of a stock or other asset is likely to decline. By purchasing a put option, you’re essentially taking out insurance against potential losses in your portfolio, while also potentially benefiting from a declining market.
Understanding the Basics of Put Options
Key Components of a Put Option
Before diving into the intricacies of put option trading, let’s first understand its fundamental components:
- Underlying Asset: This refers to the specific asset that the put option is based on, such as a stock, an index, or a commodity.
- Strike Price: The predetermined price at which the buyer can sell the underlying asset.
- Expiration Date: The final date on which the put option can be exercised.
- Premium: The price paid by the buyer to acquire the put option. This is the cost of the insurance against potential losses.
How Put Options Work: A Simplified Example
Imagine you own 100 shares of Company ABC, currently trading at $50 per share. You’re concerned about a potential decline in ABC’s stock price and wish to protect your investment. You decide to purchase a put option with a strike price of $45 and an expiration date of one month. The premium for this put option is $3. Here’s how the scenario could play out:
- Scenario 1: ABC’s stock price falls to $40: You would exercise your put option, selling your 100 shares at the strike price of $45, despite the current market price of $40. This would generate a profit of $5 per share ($45 strike price – $40 market price) minus the $3 premium, resulting in a net profit of $2 per share.
- Scenario 2: ABC’s stock price remains above $45: You wouldn’t exercise your option, as the market price is higher. You would lose the premium you paid for the option ($3 per share). However, you would still have your original 100 shares, protected from any potential decline below $45.
![How to BUY a PUT Option - [Option Trading Basics] - Tradersfly Options ...](https://i.pinimg.com/originals/52/5f/da/525fda0acf94f16c1e8a56569bf21b08.jpg)
Image: www.pinterest.cl
Types of Put Option Strategies: Tailoring Your Approach
The world of put options isn’t limited to a single strategy. There are multiple approaches you can employ, each with its own risk and reward profile. Here are some popular put option strategies:
1. Covered Put Writing: Generating Income and Limiting Losses
This strategy involves selling a put option on a stock you already own. If the stock price falls below the strike price, you are obligated to purchase the shares from the option holder. However, since you already own the shares, you can simply deliver them. This strategy generates premium income but limits potential losses. It is suitable for investors who are bullish on the underlying stock and are willing to buy more shares if the price falls.
2. Cash-Secured Put: Managing Risk and Generating Income
In this strategy, you sell a put option and deposit the equivalent cash value of the underlying stock in an account. If the stock price falls below the strike price, you are obligated to buy the shares from the option holder. The cash you’ve deposited will be used for this purchase, protecting you from potential losses. This strategy combines limited risk with potential for premium income, making it suitable for investors who are neutral or slightly bearish on the underlying asset.
3. Protective Put: Insurance Against Portfolio Losses
This strategy involves buying a put option on a stock you already own. This acts as insurance against stock price declines, with the strike price selected to cover the invested capital. A protective put strategy is suitable for investors who want to protect their portfolio against potential losses, allowing them to hold onto their existing positions while limiting downside risk.
4. Naked Put Selling: Maximum Risk, Maximum Reward
This strategy involves selling a put option without owning the underlying stock. While this offers the potential for substantial premiums, it also exposes the seller to unlimited risk, as the stock price could potentially fall indefinitely. This strategy is highly risky and should only be undertaken by experienced traders who thoroughly understand its potential consequences.
Factors to Consider Before Trading Put Options
Put options can be powerful tools, but like any financial instrument, they come with certain risks. Here are some crucial factors to consider before engaging in put option trading:
1. Market Volatility: The Fuel for Put Option Strategies
Volatility is essential for put options. Higher volatility means greater price fluctuations, which can lead to potentially larger profits for put buyers and higher premiums for put sellers. Understanding market sentiment and anticipating potential volatility swings is crucial for successful put option trading.
2. Time Decay: The Erosion of Premium
Put options are time-sensitive assets. The value of a put option decreases as the expiration date approaches. This phenomenon is known as time decay, and it’s a key element to factor into your trading decisions. With time decay working against you, it’s essential to carefully assess the remaining time until expiration and weigh it against your trading goals.
3. Strike Price: Choosing the Right Level of Protection
The strike price determines the price at which you can sell the underlying asset. Choosing the right strike price is vital to ensure you have adequate protection if the stock price falls. A higher strike price will provide more protection but may result in a higher premium. It’s crucial to balance the level of protection with the cost of acquiring the option.
4. Risk Tolerance: Understanding Your Limits
Put options can amplify potential profits and losses. It’s essential to evaluate your risk tolerance and invest only what you can afford to lose. Never trade with borrowed money or funds that are essential for your everyday needs. Remember, even experienced traders can experience losses in the market. Always develop a solid risk management plan and strictly adhere to it.
Trading Put Options
Put Options: A Powerful Tool for Strategic Investors
Put options offer a unique set of possibilities for both seasoned traders and newcomers to the financial markets. They provide a way to capitalize on market downturns, protect portfolios from losses, and even generate extra income. However, it’s essential to approach put option trading with a clear understanding of the underlying principles and the associated risks. Thorough research, careful planning, and disciplined execution are crucial aspects of successful put option trading. Like any financial tool, learning to wield the power of put options comes with dedication and practice. Whether you’re seeking to protect your existing investments, generate income, or speculate on market trends, the world of put options can open doors to new opportunities and strategies within the financial markets.
This article serves as a starting point in your journey to explore the intriguing world of put options. As you delve deeper, you’ll discover various strategies, analytical tools, and techniques that can further enhance your understanding and refine your approach. Remember, the best way to grasp the intricacies of put options is to continuously learn, practice, and, ultimately, to embrace the journey of becoming a more informed and strategic financial investor.






